INFS6023 Data Visualization
INFS6023 数据可视化
数据可视化代写 With the rapid increase in the spread of novel COVID-19 disease, many organizations, including World Health Organizations…
Part 1: Interactive data visualization related to COVID-19
第 1 部分:与 COVID-19 相关的交互式数据可视化
Summary and description of the visualization
With the rapid increase in the spread of novel COVID-19 disease, many organizations, including World Health Organizations and agencies are publishing the latest results on its impact over the last few months. The visualization from covidvisualizer.com (2020) shows real-time fatalities and trends across the world. The website uses a spinning globe to represent the world map. The data visualization is interactive, and as the user hovers through the visual can click to view the data analysis of a specific country. Users use these visuals to see how various countries are recording cases of coronavirus.
At the bottom of COVID-19 data visualization, there is a real-time counter of worldwide cases. Three variables are being measured and compared, including active infections, the number of deaths, and recoveries. On a click, the data analysis of a specific country pops-out indicating the country name on the top, the total number of cases, reported active cases, and additional cases in the last few hours. The pop-up also indicates the number of deceased and recovered. Finally, the pop-up has a line graph showing the trend of the three variables, including total cases, deaths, and recovered. Overall, data visualization is a perfect presentation of the number of COVID-19 spreads in the world.
The data visualization is easy to use, understand, and interpret because it is mapped on a globe. The key takeaway is that data visualization should depict the objective of the data. For instance, covidvisualizer.com intends to show the global trend of the disease, and hence it is using graphics that represent the globe.
可视化的摘要和描述 数据可视化代写
译文:随着新型 COVID-19 疾病传播的迅速增加,包括世界卫生组织和机构在内的许多组织都在发布有关其在过去几个月中的影响的最新结果。 covidvisualizer.com (2020) 的可视化显示了世界各地的实时死亡人数和趋势。该网站使用一个旋转的地球仪来表示世界地图。数据可视化是交互式的,当用户在视觉上悬停时,可以点击查看特定国家的数据分析。用户使用这些视觉效果来了解各个国家如何记录冠状病毒病例。
在 COVID-19 数据可视化的底部,有一个全球病例的实时计数器。正在测量和比较三个变量,包括活跃感染、死亡人数和康复人数。单击一下,特定国家/地区的数据分析会弹出,在顶部显示国家/地区名称、病例总数、报告的活跃病例以及过去几个小时内的其他病例。弹出窗口还会显示死者和康复者的人数。最后,弹出窗口有一个折线图,显示三个变量的趋势,包括病例总数、死亡人数和康复人数。总体而言,数据可视化是对全球 COVID-19 传播数量的完美呈现。 数据可视化代写
数据可视化易于使用、理解和解释,因为它映射在地球上。关键要点是数据可视化应该描述数据的目标。例如,covidvisualizer.com 旨在显示该疾病的全球趋势,因此它使用代表全球的图形。
Analysis of visuals
The visuals used geographical scatter plots to present the data. Quantitative data was used in the analysis and presentation of data. For instance, the United States is leading with over 700,000 active cases (Covidvisualizer.com, 2020). The country records an average of 1000 cases in the last 24 hours. The trend line shows that the number of cases has been on the rise since mid-January 2020. Other most affected countries include France, Italy, and Spain, with 159,877, 187,327, and 208,389, respectively. In each of these countries, the number of cases is on the rise, the first case was reported.
In this regard, for the visuals to present accurate information to the audience, they have utilized various forms and elements of data visualization, including positioning, scale, decluttering, use of graphs, color, and emphasis. The visual used world globe to position that data analysis. The globe spins, and the user can drag it to any desired position. The positioning enhances the visual perception of the information presented. That is the data intended to show the world distribution of the pandemic. The visuals use the percentage of deaths and recoveries to the total cases of infection of a particular country. Also, it is not cluttered with data as each geographical scatter plot represents one country. Thus, the number of scatter plots is as many as the number of countries, making a clear distinction to the user.
视觉分析 数据可视化代写
译文:视觉效果使用地理散点图来呈现数据。定量数据用于数据的分析和呈现。例如,美国处于领先地位,有超过 700,000 个活跃病例(Covidvisualizer.com,2020)。该国在过去 24 小时内平均记录了 1000 例病例。趋势线显示,自 2020 年 1 月中旬以来,病例数一直在上升。其他受影响最严重的国家包括法国、意大利和西班牙,分别为 159,877、187,327 和 208,389。在这些国家中的每一个,病例数都在上升,报告了第一例。
在这方面,为了让视觉向观众呈现准确的信息,他们利用了数据可视化的各种形式和元素,包括定位、比例、整理、图表的使用、颜色和强调。视觉使用世界地球仪来定位数据分析。地球仪旋转,用户可以将其拖动到任何所需位置。定位增强了所呈现信息的视觉感知。这些数据旨在显示大流行的世界分布。视觉效果使用死亡和康复占特定国家感染病例总数的百分比。此外,由于每个地理散点图代表一个国家,因此它不会被数据杂乱无章。因此,散点图的数量与国家的数量一样多,对用户进行了明确的区分。 数据可视化代写
The graph presentation of the data is embedded in each scatter plots of countries and display on a click.
It uses a line graph of time against the number of active cases, deaths, and recoveries. Additionally, the visual uses a red color to indicate the severity of the pandemic in various countries. Hot red is an indication of a high number of infection cases, while a dull red color indicates a low number of infections. The color gradient is also a depiction of an emphasis on the number of cases reported. In this respect, the United States has the highest number of infection cases, and Yemen has the least infections as of 23 April 2020. The color makes the geographical scatter plot intuitive in the interpretation and hence easier to understand and interpret.
In this context, COVID-19 visuals can be evaluated with the various frameworks of data visualization. Data visualization can take the forms and function of being static, exploratory, explanatory, and interactive (Schwabish, 2014). Also, the visuals can be declarative, conceptual, exploratory, and data-driven. COVID-19 visualization presented is interactive in that the globe is spinning, the user can click and drag it to any position, and clicking on the map on a particular country pops out the analysis of COVID-19 cases reported. Interactive visualization allows the user to interact with a story presented. Therefore, the visuals are the function of explanatory in that the geographical scatter us color to create emphasis, and the pops out have line graphs that indicate whether cases are rising or falling in a particular country.
数据的图形表示嵌入在每个国家/地区的散点图中,单击即可显示。
译文:它使用时间线图与活跃病例、死亡人数和康复人数之间的关系。此外,视觉效果使用红色来表示各个国家大流行的严重程度。热红色表示感染病例数量较多,而暗红色表示感染数量较少。颜色渐变也是对报告病例数量的强调。在这方面,截至 2020 年 4 月 23 日,美国的感染病例数最多,也门的感染人数最少。颜色使地理散点图在解释上更加直观,因此更易于理解和解释。 数据可视化代写
在这种情况下,可以使用各种数据可视化框架来评估 COVID-19 视觉效果。数据可视化可以采用静态、探索性、解释性和交互性的形式和功能(Schwabish,2014)。此外,视觉效果可以是声明性的、概念性的、探索性的和数据驱动的。呈现的 COVID-19 可视化是交互式的,因为地球在旋转,用户可以单击并将其拖动到任何位置,单击特定国家/地区的地图会弹出报告的 COVID-19 病例分析。交互式可视化允许用户与呈现的故事进行交互。因此,视觉效果是解释性的,因为地理分散我们的颜色来创造重点,弹出的线条图表明特定国家的病例是上升还是下降。
However, the visual is neither static nor exploratory.
Static visuals are presented using forms that are not interactive, such as line graphs, bars, and charts on a pdf file or image. They lead users to discover their own stories as they analyze the figures, pie charts, bars, etc. The COVID-19 presentation, in this case, would be static if the data visualization image is taken. The visuals are not a function of exploratory, which requires the user to generate their hypothesis and stories using the representation.
Additionally, the visuals can be evaluated using Berinato’s framework of data visualization (Berinato, 2016). The COVID-19 visual representation is data-driven and hence involve everyday DataViz. It is not conceptual because it does not intend to present an idea. On the other hand, it is neither declarative nor exploratory because it is not affirming or confirming any phenomena. Declarative visualization is used to document or design information while exploratory establish the relationship that exists between two variables. COVID-19 visuals seek to inform on the number of in various countries and hence indicate the rate of spread to tell on decision-making.
然而,视觉既不是静态的,也不是探索性的。
译文:静态视觉效果使用非交互式形式呈现,例如 pdf 文件或图像上的折线图、条形图和图表。它们引导用户在分析数字、饼图、条形图等时发现自己的故事。在这种情况下,如果采用数据可视化图像,则 COVID-19 演示文稿将是静态的。视觉效果不是探索性的功能,它要求用户使用表示生成他们的假设和故事。 数据可视化代写
此外,可以使用 Berinato 的数据可视化框架 (Berinato, 2016) 评估视觉效果。 COVID-19 视觉表示是数据驱动的,因此涉及日常 DataViz。它不是概念性的,因为它不打算提出一个想法。另一方面,它既不是陈述性的,也不是探索性的,因为它不肯定或证实任何现象。声明性可视化用于记录或设计信息,而探索性可视化用于建立两个变量之间存在的关系。 COVID-19 视觉效果旨在了解各个国家/地区的人数,从而表明传播速度以告知决策。
Designing effective visualization
Data visualization is more than just displaying data. It is also how the data is showing in ways that make it easier for users to understand and interpret (Tanahashi, Leaf, & Ma, 2016). The COVID-19 data presentation is useful in visualization. The information is presented using a form that tells the story by use of geographical scatter plot on countries on a spinning globe. The visuals intend to tell the story of the world distribution of COVID-19 infections and the rate of spread. The visuals are intuitive through graphics mapping of the globe and countries that cater to the user’s domain-specific mental model. The use of geophysical scatter on countries facilitate interpretation. Similarly, the use of three-dimension mapping that animates the world increases user intuition in understanding and interpretation.
The intuition created by global map visuals is complemented by the use of color. The visuals also use a red color but with various color gradients depending on the number of infections and attribute to the pandemic. That is, hot red color indicates a high rate of pandemic infections, and dull red color indicates a low rate of infection.
However, there are visual designs that need improvement. It is not apparent that the visuals are interactive. The visuals should add hovering interactivity to notify and enable the user to trace the data of interest. Also, the visual could have used a better form to represent active cases, deaths, and recoveries. The use of ratios to indicate inactive cases and percentages in deaths and recoveries does not give a clear visual interpretation. For instance, active cases are presented as a ratio of the total number cases without further simplification. It thus becomes difficult for the users to, at a glance, understand the ratio. The number of deaths and recoveries are also confusing because they do not indicate how the rate is calculated. The problems could be solved by the use of pie charts be they give clear comparison between various variables.
设计有效的可视化 数据可视化代写
译文:数据可视化不仅仅是显示数据。这也是数据的显示方式,让用户更容易理解和解释(Tanahashi、Leaf 和 Ma,2016 年)。 COVID-19 数据表示在可视化中很有用。该信息使用一种形式呈现,该形式通过使用旋转地球上国家的地理散点图来讲述故事。视觉效果旨在讲述 COVID-19 感染的世界分布和传播速度的故事。通过满足用户特定领域心理模型的全球和国家/地区的图形映射,视觉效果非常直观。对国家使用地球物理散射有助于解释。同样,使用动画世界的三维映射增加了用户在理解和解释方面的直觉。
颜色的使用补充了全局地图视觉创建的直觉。视觉效果也使用红色,但具有各种颜色渐变,具体取决于感染数量和大流行的属性。也就是说,热红色表示大流行感染率高,暗红色表示感染率低。 数据可视化代写
但是,有些视觉设计需要改进。视觉效果是交互式的并不明显。视觉效果应添加悬停交互性以通知用户并使用户能够跟踪感兴趣的数据。此外,视觉效果可以使用更好的形式来表示活跃病例、死亡和康复。使用比率来表示非活跃病例以及死亡和康复的百分比并没有给出清晰的视觉解释。例如,在没有进一步简化的情况下,活动案例显示为案例总数的比率。因此,用户难以一目了然地理解该比率。死亡人数和康复人数也令人困惑,因为它们没有说明该比率是如何计算的。这些问题可以通过使用饼图来解决,因为它们可以清楚地比较各种变量。
Ethical implication of the visualization
According to the UNESCO International Bioethics Committee (IBC) and UNESCO World Commission on the Ethics of Scientific Knowledge and Technology (COMEST) (2020), there are potential bioethical implications in COVID-19 data visualization. For instance, if the visualization compares how COVID-19 affect women and men may mislead that the disease is more prevalent to a particular gender it is because not scientifically proven. It is also unethical to compare the number of deaths caused by the pandemic across various countries. Additionally, the data used to make visuals should be from a reliable source so that misinformation is not published and hence lead to wrong interpretations. Ethics in data visualization seeks to protect the public from making poor decisions based on bad data.
可视化的伦理意义
译文:根据联合国教科文组织国际生物伦理委员会 (IBC) 和联合国教科文组织世界科学知识与技术伦理委员会 (COMEST) (2020) 的说法,COVID-19 数据可视化具有潜在的生物伦理意义。例如,如果可视化比较 COVID-19 如何影响女性和男性,可能会误导该疾病在特定性别中更为普遍,这是因为未经科学证实。比较各国因大流行造成的死亡人数也是不道德的。此外,用于制作视觉效果的数据应该来自可靠的来源,以免发布错误信息,从而导致错误的解释。数据可视化中的伦理旨在保护公众免于基于不良数据做出错误决策。 数据可视化代写
Potential data quality issues
Lastly, COVID-19 data visualization is not immune to data quality issues. The data used may be incomplete because some COVID-19 cases are inaccessible or unreported. It is mainly the case in Africa, where there are inadequate healthcare facilities and testing kits. The data recorded and presented is for the cases captured, but the actual figure on the ground is unknown.
潜在的数据质量问题 数据可视化代写
译文:最后,COVID-19 数据可视化也无法避免数据质量问题。使用的数据可能不完整,因为某些 COVID-19 病例无法访问或未报告。这种情况主要发生在非洲,那里的医疗设施和检测工具不足。记录和呈现的数据是针对捕获的案件,但实地的实际数字未知。
Part 2: Data source analysis and visualization
第 2 部分:数据源分析和可视化
Description of the data source
Link to the data source: https://data.census.gov/cedsci/table?q=Income%20&tid=ACSST1Y2018.S1901&t=Income%20%28Households,%20Families,%20Individuals%29&vintage=2018&hidePreview=false
The data source is the United States Census Bureau (2018). The bureau is tasked with the enumeration of the number of people in the United States. Besides the decennial census, the bureau also collects data through over 130 surveys and programs, including economic census, community survey, and current population survey. The data collected during the census helps the government policy planning and decisions on school facilities, hospitals, transport infrastructure, security, social services, among others. Census Bureau provides comprehensive, timely, and accurate that can be used to explain business and social issues.
Additionally, Census Bureau is a mandate of the U.S constitution that census should be conducted every ten years to count for all people, both citizens and non-citizens in the country, and also carry out other surveys. People are obligated by law to respond to any government survey so that the government can get a complete and accurate population and other critical characteristics about society. Correct census data is used as a basis for fair political representation and plays an essential role in planning for public services. These make the data source important for this data visualization.
数据源描述 数据可视化代写
译文:数据来源链接:https://data.census.gov/cedsci/table?q=Income%20&tid=ACSST1Y2018.S1901&t=Income%20%28Households,%20Families,%20Individuals%29&vintage=2018&hidePreview=false
数据来源是美国人口普查局 (2018)。该局的任务是统计美国的人数。除了十年一次的人口普查外,该局还通过 130 多项调查和计划收集数据,包括经济普查、社区调查和当前人口调查。人口普查期间收集的数据有助于政府在学校设施、医院、交通基础设施、安全、社会服务等方面的政策规划和决策。人口普查局提供全面、及时和准确的信息,可用于解释商业和社会问题。
此外,人口普查局是美国宪法的一项授权,即应每十年进行一次人口普查,以统计该国公民和非公民的所有人,并进行其他调查。法律规定人们有义务对任何政府调查做出回应,以便政府能够获得完整而准确的人口和其他社会关键特征。正确的人口普查数据被用作公平政治代表的基础,并在公共服务规划中发挥重要作用。这些使数据源对于此数据可视化很重要。 数据可视化代写
Justification of the selection
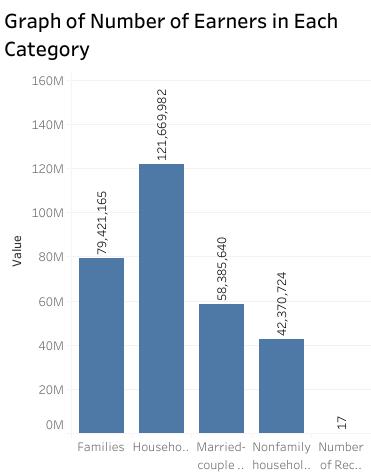
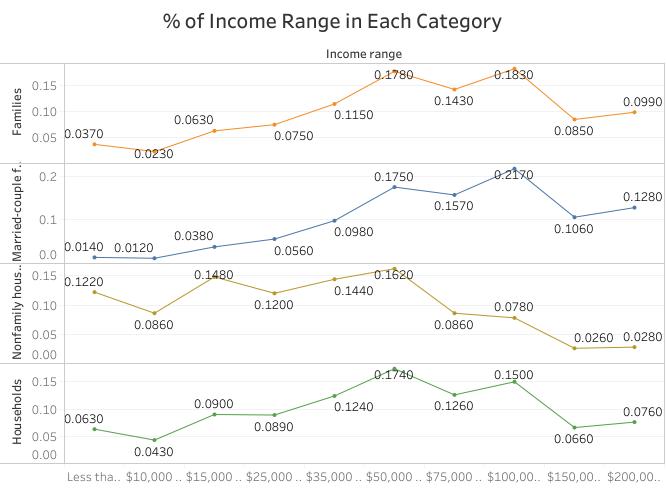
The data for income in the past 12 months in 2018 was selected. The information is an accurate record of income for households, families, married-couple families, and nonfamily households (Groves, 2011). The income levels of various categories are measured in ranges. It starts with those that earn less than $10,000 to those that earn $200,000 and above per annum (United States Census Bureau, 2018). The data is essential to the government, policymakers, businesses, and other non-government agencies. The reason being it touches on the core issue that impacts on the public social affairs.
Thus, the selection of this data allows me to explore how income is distributed across the United States and which group earns enough or little. The analysis will also assist in understanding the source of income disparity and policy measures that can be taken. Besides analyzing and interpreting the data, I made the selection because it has several variables and categories for comparison and hence gives me a chance to explore and practice various concepts of data visualization.
Therefore, the data visualization of income in 2018 has some benefits to the data source with planning for minimum wages and social benefits as well as other economic planning by the government. The visuals will show the range of earning each category of people and the percentage in the population. One can know which group has high earning in the population and which earing level has the majority. Thus, the government can use data visualization to plan for an economic stimulus program that can elevate the income of a particular group. For instance, if a nonfamily household is a category that has a high number of people earning less than $50,000 per annum, then research can be conducted to establish the reason for the disparity.
选择理由
译文:选取了2018年过去12个月的收入数据。该信息是家庭、家庭、已婚夫妇家庭和非家庭家庭收入的准确记录(格罗夫斯,2011 年)。各种类别的收入水平以区间衡量。从年收入低于 10,000 美元的人到年收入 200,000 美元及以上的人(美国人口普查局,2018 年)。这些数据对政府、决策者、企业和其他非政府机构至关重要。究其原因,是触及了影响公共社会事务的核心问题。 数据可视化代写
因此,选择这些数据使我能够探索美国各地的收入如何分配以及哪个群体的收入足够或很少。该分析还将有助于了解收入差距的来源和可以采取的政策措施。除了分析和解释数据,我做出选择是因为它有几个变量和类别可供比较,因此让我有机会探索和实践数据可视化的各种概念。
因此,2018年收入的数据可视化对数据源有一定的好处,包括最低工资和社会福利的规划以及政府的其他经济规划。视觉效果将显示每类人的收入范围和人口百分比。人们可以知道人口中哪个群体的收入高,哪个收入水平占多数。因此,政府可以使用数据可视化来规划可以提高特定群体收入的经济刺激计划。例如,如果一个非家庭家庭是一个拥有大量年收入低于 50,000 美元的人的类别,则可以进行研究以确定差异的原因。
Data visualization frameworks regarding the data source
The income data from the census bureau is preprocessed. The data can be interpreted as it is without making visualization because it presented in categories that easier to understand. The data source is static as it is from the source. As a user, I am left to read the data and come up with an interpretation. As such, the data can be used for exploration where the user is allowed to transfer and interface with the data to generate interpretations from it. Data that is exploratory can be raw or preprocessed so that the user can use it for further inquiries. The decision which can be made from this data is fact-based because the data is from a defined population.
On the other hand, the income data can be evaluated based on Berinato’s framework. The presentation is data-driven, where the census bureau presented findings from a survey to inform the government on the income levels and disparities in the population. It is also declarative by affirming the various income levels in multiple categories of households and families. It declares the findings of the bureau survey on income characteristics of the population.
关于数据源的数据可视化框架 数据可视化代写
译文:来自人口普查局的收入数据经过预处理。数据可以按原样解释,无需进行可视化,因为它以更容易理解的类别呈现。数据源是静态的,因为它来自源。作为用户,我只能阅读数据并做出解释。因此,数据可用于探索,允许用户传输数据并与数据交互以从中生成解释。探索性数据可以是原始数据或预处理数据,以便用户可以将其用于进一步查询。可以根据这些数据做出的决定是基于事实的,因为数据来自确定的人群。
另一方面,收入数据可以基于 Berinato 的框架进行评估。该演示文稿是数据驱动的,人口普查局在其中展示了一项调查的结果,以向政府通报收入水平和人口差距。它还通过确认多个类别的家庭和家庭的各种收入水平来声明。它宣布了该局关于人口收入特征的调查结果。
Additionally, some frameworks can be used to explain the visualization of income data.
The data visualization should be interactive to allow the user to be intuitive with the story. Thus, the visuals will be explanatory to the government, and other agencies can use them to identify how income is distributed across households and families.
Furthermore, data visualization should not only be concerned with presenting data but also the quality of the visuals used. A single color should be used to reduce visual illusion and misconception that can emerge from a mix of different colors. The characteristics of data itself dictate how color is perceived. The labeling should neither clutter visualization nor provide insufficient information. Labels should be put alongside and well-oriented to each bar or chart it represents. Cluttering of information may make the information hard to interpret, and insufficient information makes the visuals ambiguous. Visual quality facilitates understandability and intuitive interaction and interpretation of the data.
Overall, data and visual ethics are essential to reduce the chances of misrepresentation and misinformation in decision making. If the visual fails to give a clear distinction between households and families, the user may use them interchangeably, which is misleading. The number of homes is not included in the families or vice versa. The visuals can have a separate data presentation showing the comparison between various categories before narrowing down to comparing the income differences between the various groups. It will give the visual implication of the differences between the three groups. It will also be unethical to compare the two categories leaving others. The four income groups should be visualized together to enhance the complete view of the population. Ethical considerations mitigate the misinformation of the public or stakeholders who rely on the visuals to make decisions.
此外,一些框架可用于解释收入数据的可视化。
译文:数据可视化应该是交互式的,以允许用户直观地了解故事。因此,视觉效果将向政府解释,其他机构可以使用它们来确定收入如何在家庭和家庭之间分配。 数据可视化代写
此外,数据可视化不仅应该关注呈现数据,还应该关注所使用的视觉效果的质量。应使用单一颜色来减少因混合不同颜色而产生的视觉错觉和误解。数据本身的特性决定了如何感知颜色。标签既不应使可视化混乱,也不应提供不足的信息。标签应与它所代表的每个条形图或图表并排放置并定位良好。信息混乱可能使信息难以解释,信息不足使视觉模糊。视觉质量有助于数据的可理解性和直观的交互和解释。
总体而言,数据和视觉伦理对于减少决策中出现虚假陈述和错误信息的可能性至关重要。如果视觉上没有明确区分家庭和家庭,用户可能会互换使用它们,这是一种误导。家庭数量不包括在家庭中,反之亦然。在缩小到比较不同组之间的收入差异之前,视觉效果可以有单独的数据呈现,显示不同类别之间的比较。它将给出三组之间差异的视觉含义。比较离开其他类别的两个类别也是不道德的。应将四个收入群体一起可视化,以增强对人口的整体看法。道德考虑减轻了依赖视觉做出决策的公众或利益相关者的错误信息。
Part 3: Tableau visualization
第 3 部分:表格可视化
References
Berinato, S. (2016). Good charts: The HBR guide to making smarter, more persuasive data visualizations. Harvard Business Review Press.
Covidvisualizer.com. (2020). COVID-19. Retrieved from https://www.covidvisualizer.com/
Groves, R. (2011). The Credibility of Government Statistics; Trust in their Source. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved from https://www.census.gov/newsroom/blogs/director/2011/04/the-credibility-of-government-statistics-trust-in-their-source.html
IBC & COMEST. (2020). Statement on COVID-19: Ethical Considerations from a global perspective. Unesco. Retrieved from https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000373115
Schwabish, J. A. (2014). An economist’s guide to visualizing data. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 28(1), 209-34.
Tanahashi, Y., Leaf, N., & Ma, K. L. (2016). A study on designing effective introductory materials for information visualization. In Computer Graphics Forum (Vol. 35, No. 7, pp. 117-126).
United States Census Bureau. (2018). Income in the past 12 months (in 2018 inflation-adjusted dollars. Retrieved from https://data.census.gov/cedsci/table?q=Income%20and%20Earnings&hidePreview=false&t=Income%20and%20Earnings&tid=ACSST1Y2018.S1901&vintage=2018



