CP5631 Assignment – Networking Case Study
Networking Case代写 Networking Case Study This project is to evaluate and redesign the networks for a major Australian data analysis company

PART 1 – Executive summary Networking Case代写
1.Purpose
This project is to evaluate and redesign the networks for a major Australian data analysis company which is planning to open new branches in San Francisco and Osaka. We need to make use of new equipment and existing contracts and hardware to construct the networks and maintain fiber optic leased line WAN links between sites. For part2, we need to define the specifications in this network and draw the network topology diagram that it is convenient to reflect the structural relationships between entities in the network.
For part3, we aim to subnet the network using VLSM, and assign IP addresses to the corresponding devices.
As for part4, we hope to research and select suitable communication equipment with a weighted scoring mode(WSM) through some performance indicators such as feasibility, efficiency, etc. In addition, we want to calculate the total prices of all devices and the total cost for hardware devices.
2.Scope
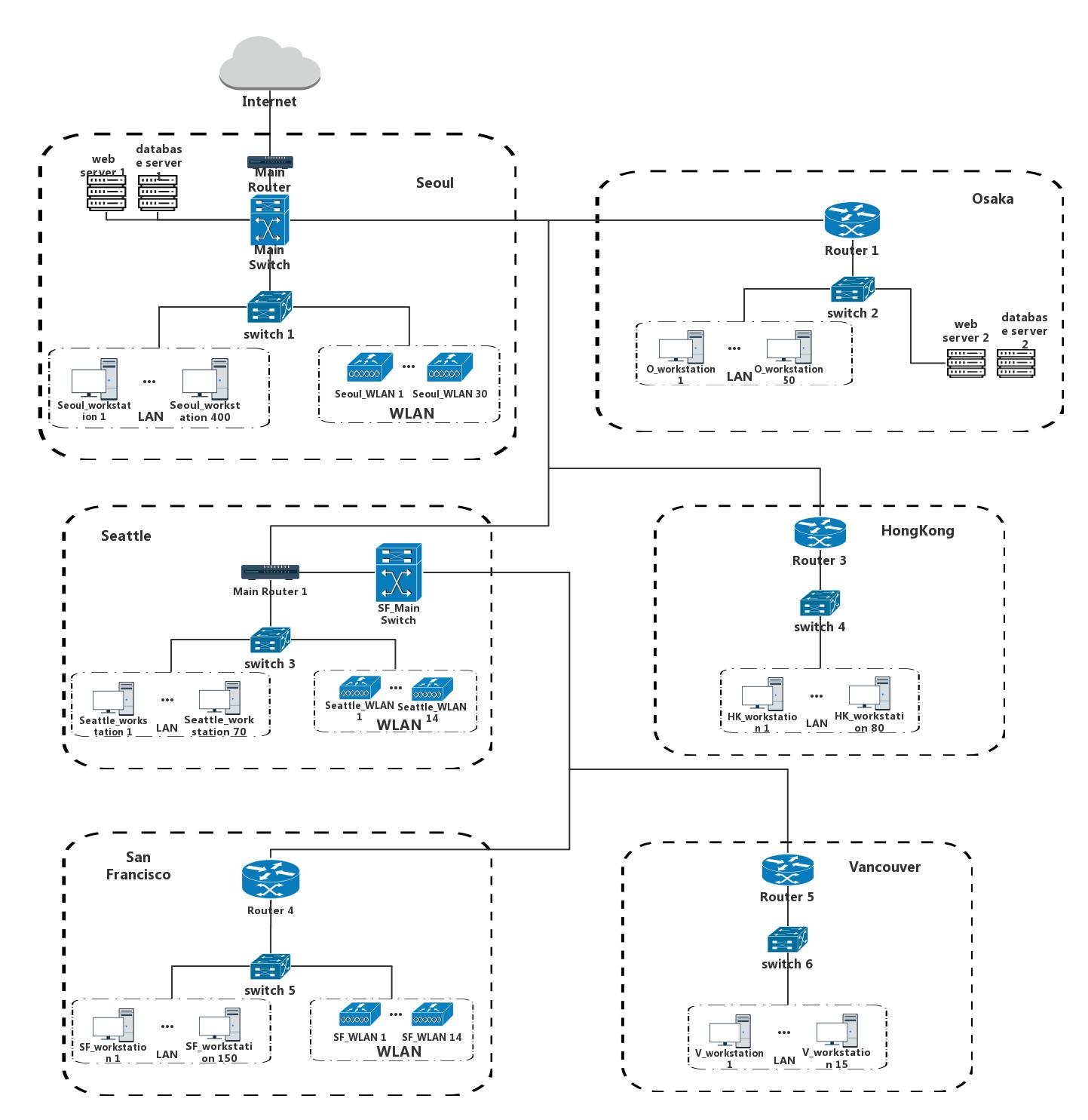
For the part2, it is obvious that we could get a network topology diagram with well-defined facilities, which is an intuitive embodiment of the solution, and a more intuitive understanding of the network architecture. The diagram makes it easy to analyze the structural transformation.
For the part3, we are able to get three tables including Subnets, Router Interfaces and Servers. These tables are capable of recording all details in the configuration of Subnets, Router Interfaces and Servers.
For the part4, we will research and submit a project procurement plan for the San Francisco networks. Through this plan, we could know how to choose appropriate devices by WDM with hardware resource requirements. In the end, we calculate the total cost of hardware.
3.Objectives Networking Case代写
The objective of part 2 is to draw the network topology diagram for this communication network of the data analysis company which includes all the facilities in the network, such as workstations, severs, routers, switches, and wireless access points and etc. This diagram should be finished firstly before following work within 1 day. Because this diagram will help with the following parts in this project.
As for part3, the objectives are three tables which provide details of Subnets, Router Interfaces and Servers in the whole network, respectively. We need to define all Subnet name, subnet address, subnet mask, first useable address, last useable address, broadcast address, static address range and DHCP address range for these facilities in Subnets table.
As for part4, the objective is conducting a project procurement plan for the San Francisco networks which are consist of devices including routers, switches, and wireless access points. This work through which that we have made the best choice within the budget should be finished before the network deployment.
PART 2 – Network specifications and diagram
PART 3 – Subnet the network using VLSM, and assign IP addresses to the appropriate devices. Networking Case代写
1.Subnet table
| subnet name | subnet address | subnet mask | first useable address | last useable address |
| Seoul | 104.200.16.24 | /22 | 104.200.16.25 | 104.200.20.22 |
| Seattle | 104.200.23.24 | /24 | 104.200.23.25 | 104.200.24.22 |
| San Francisco | 104.200.20.24 | /23 | 104.200.20.25 | 104.200.22.22 |
| Osaka | 104.200.24.24 | /25 | 104.200.24.25 | 104.200.23.22 |
| Hong Kong | 104.200.22.24 | /24 | 104.200.22.25 | 104.200.23.22 |
| Vancouver | 104.200.24.152 | /27 | 104.200.24.153 | 104.200.24.182 |
Subnet table 1
| subnet name | broadcast address | static address range | DHCP address range |
| Seoul | 104.200.20.23 | 104.200.16.25 – 104.200.20.22 | 104.200.16.25 – 104.200.20.22 |
| Seattle | 104.200.24.23 | 104.200.23.25 – 104.200.24.22 | 104.200.23.25 – 104.200.24.22 |
| San Francisco | 104.200.22.23 | 104.200.20.25 – 104.200.22.22 | 104.200.20.25 – 104.200.22.22 |
| Osaka | 104.200.24.151 | 104.200.24.25 – 104.200.24.150 | 104.200.24.25 – 104.200.24.150 |
| Hong Kong | 104.200.23.23 | 104.200.22.25 – 104.200.23.22 | 104.200.22.25 – 104.200.23.22 |
| Vancouver | 104.200.24.183 | 104.200.24.153 – 104.200.24.182 | 104.200.24.153 – 104.200.24.182 |
Subnet table 2
2.Router Interfaces Networking Case代写
| Router Interfaces | |||
| Location | interface | IP address | subnet mask |
| Seoul | LAN & WLAN interface | 104.200.16.25 | /22 |
| Seattle | LAN & WLAN interface | 104.200.23.25 | /24 |
| San Francisco | LAN & WLAN interface | 104.200.20.25 | /23 |
| Osaka | LAN interface | 104.200.24.25 | /25 |
| Hong Kong | LAN interface | 104.200.22.25 | /24 |
| Vancouver | LAN interface | 104.200.24.153 | /27 |
3.Servers
| Servers | |||
| Location | server name | IP address | subnet mask |
| Seoul | web server | 104.200.20.22 | /22 |
| Seoul | database server | 104.200.20.21 | /22 |
| Osaka | web server | 104.200.24.150 | /25 |
| Osaka | database server | 104.200.24.149 | /25 |
PART 4 – Research and source appropriate devices justifying choices (feasibility, efficiency, etc.) Networking Case代写
In order to construct the network in San Francisco, we aim to choose some devices, such as routers, switches, and wireless access points. In addition, we need to conduct a project procurement plan for choosing the best performance devices which provide a good quality of service to wired and wireless users. Specifically, our project plan and final recommendations which are based on a Weighted Decision Matrix(WDM) compared with five devices from each category.
1.Weighted Decision Matrixfor routers:
Router A Weighted Decision Matrix
| Router A Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Router A score / 1-5 | Router A weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 5 | 20 |
| 2 | Firewall | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 3 | Routing Exchange Protocol | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 4 | Brand Value | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 6 | Total Score | 66 | ||
Router B Weighted Decision Matrix
| Router B Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Router B score / 1-5 | Router B weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 2 | 8 |
| 2 | Firewall | 3 | 5 | 15 |
| 3 | Routing Exchange Protocol | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 4 | Brand Value | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 6 | Total Score | 53 | ||
Router C Weighted Decision Matrix
| Router C Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Router C score / 1-5 | Router C weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| 2 | Firewall | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | Routing Exchange Protocol | 4 | 5 | 20 |
| 4 | Brand Value | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 6 | Total Score | 57 | ||
Router D Weighted Decision Matrix
| Router D Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Router D score / 1-5 | Router D weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 5 | 20 |
| 2 | Firewall | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | Routing Exchange Protocol | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| 4 | Brand Value | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 6 | Total Score | 54 | ||
Router E Weighted Decision Matrix
| Router E Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Router E score / 1-5 | Router E weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 2 | Firewall | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | Routing Exchange Protocol | 4 | 5 | 20 |
| 4 | Brand Value | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 6 | Total Score | 65 | ||
Some typical priorities and attributes of 5 brand routers are taken into consideration in the weighted decision matrixes. We could draw some conclusions from the blow weighted decision matrixes. The price and the performance of routing exchange protocol are most important. So, we choose brand A router as our router in project, since they are the highest score in the WDM.
2.Weighted Decision Matrixfor switches:
Switch A Weighted Decision Matrix
| Switch A Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Switch A score / 1-5 | Switch A weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 2 | 8 |
| 2 | BackPlane Capacity | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | Switch Capability | 4 | 5 | 20 |
| 4 | error rate | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 1 | 4 | 4 |
| 6 | Total Score | 53 | ||
Switch B Weighted Decision Matrix
| Switch B Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Switch B score / 1-5 | Switch B weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| 2 | BackPlane Capacity | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | Switch Capability | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 4 | error rate | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 6 | Total Score | 45 | ||
Switch C Weighted Decision Matrix
| Switch C Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Switch C score / 1-5 | Switch C weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 2 | BackPlane Capacity | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 3 | Switch Capability | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| 4 | error rate | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 6 | Total Score | 55 | ||
Switch D Weighted Decision Matrix
| Switch D Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Switch D score / 1-5 | Switch D weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| 2 | BackPlane Capacity | 3 | 5 | 15 |
| 3 | Switch Capability | 4 | 5 | 20 |
| 4 | error rate | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 6 | Total Score | 56 | ||
Switch E Weighted Decision Matrix
| Switch E Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | Switch E score / 1-5 | Switch E weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 2 | BackPlane Capacity | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 3 | Switch Capability | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 4 | error rate | 3 | 5 | 15 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| 6 | Total Score | 62 | ||
The price and switch capability are two significant indicators. From the 5 above weighted decision matrixes for switches, we choose switch E as our devices, because the switches of E brand are suitable for the price, switch capability as well as error rate. Networking Case代写
3.Weighted Decision Matrixfor wireless access points(WAP):
WAP A Weighted Decision Matrix
| WAP A Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | WAP A score / 1-5 | WAP A weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| 2 | security | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | speed | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 4 | Coverage | 4 | 5 | 20 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| 6 | Total Score | 56 | ||
WAP B Weighted Decision Matrix
| WAP B Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | WAP B score / 1-5 | WAP B weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 2 | security | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | speed | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 4 | Coverage | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 6 | Total Score | 53 | ||
WAP C Weighted Decision Matrix
| WAP C Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | WAP C score / 1-5 | WAP C weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 2 | 8 |
| 2 | security | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 3 | speed | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 4 | Coverage | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| 6 | Total Score | 56 | ||
WAP D Weighted Decision Matrix
| WAP D Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | WAP D score / 1-5 | WAP D weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 2 | security | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | speed | 3 | 4 | 12 |
| 4 | Coverage | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| 6 | Total Score | 59 | ||
WAP E Weighted Decision Matrix
| WAP E Weighted Decision Matrix | ||||
| NO. | priorities and attributes | weight score / 1-5 | WAP E score / 1-5 | WAP E weighted score |
| 1 | Price | 4 | 5 | 20 |
| 2 | security | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 3 | speed | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| 4 | Coverage | 4 | 3 | 12 |
| 5 | Maintenance Costs | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| 6 | Total Score | 56 | ||
The price and Coverage are the most significant indicators of choosing wireless access points(WAP). The WAP D is the best choice, whose total weighted score is the highest. Because the price of these devices is lower and coverage area is wider.
4.prices of all devices and the total cost Networking Case代写
| Total Cost of Hardware in San Francisco | ||||
| Devices Name | Unit Price/$ | Number | Amount/$ | total expenses/$ |
| Router A | 707.94 | 2.00 | 1415.88 | |
| Switch E | 601.00 | 2.00 | 1202.00 | |
| WAP D | 99.99 | 30.00 | 2999.70 | 5617.58 |
PART 5 – Cloud computing proposal Networking Case代写
We propose that it is better for this data analytics company to adopt the second recommendation that is replacing ALL workstations within the organisation with thin clients, which will access a desktop environment provided by a private cloud infrastructure, created in-house and based in Seoul. Here are some reasons below:
From the perspective of reducing costs, the third recommendation is the worst among these three recommendation. Networking Case代写
Because the company needs to pay $850 per workstation, per year, for hardware and service. The total cost of workstations is almost $650,000 per year, which is a huge expense. In addition, each workstation currently consumes 230 kWh per year of electricity. For more than 700 workstations, this will consume a lot of electricity and bring extra cost of electricity power. However, if we replace all workstations within the organisation with thin clients, which provided by a cloud service provider such as Amazon or Alibaba, the company is just to pay the service fee of EC2. Take an example to illustrate, the You could save 58% a year by moving all infrastructure of the company to AWS. Three-year total savings would be $ 20,686,329, which is calculated by Amazon [1]. It also saves the company’s overhead on electricity through this way.
However, from the point of data security, whether the enterprise-specific data viewing and control is truly owned by the Australian data analysis company [2].
In order to prevent suppliers from facing certain uncertainties which will cause data loss, we will still back up on our own computers for the company. This is a waste of resources. Another point is that if the company utilize a public cloud, then the vendor is not serving a certain enterprise. When multiple enterprises are running, and their application system performance will be processed at the peak time, the company’s web services will be affected.
To address these conflicts among reducing the cost and data security, we propose that the company could replace all workstations with thin clients, which will access a desktop environment provided by a private cloud infrastructure, created in-house and based in Seoul. Although the cost to establish a private cloud is relatively high, such as upfront costs, usage fees of maintenance and management resources, the private cloud is built for the company, and the private cloud’s servers are still behind an external firewall, and database server of this company stays behind another firewall, giving this data double security [3]. In the long run, this proposal will reduce the cost in hardware.
Here are also some advantages by adopting the second recommendation:
- When the company’s on-premise increases capacity, it will increase costs because the enterprise needs to upgrade the data center’s power and cooling equipment to accommodate additional rack equipment or build a new data center. Adopting a hybrid deployment approach is a viable option that does not affect existing operations. Choosing a managed cloud that supports bare metal and extends the on-premises network can allow reuse of existing technologies and tools[4].
- Directly accessible, on-premises private infrastructure.
- Not subject to the restrictions of the public Internet. This greatly reduces access time and latency compared to public cloud services.
- The ability to have a field computing infrastructure capable of supporting the average workload of the business while retaining the ability to leverage the public cloud to address failover environments where workloads exceed the computing power of private cloud components.
To sum up, for a long time, it is best choice for the data analysis company to replace all workstations within the organisation with thin clients, which will access a desktop environment provided by a private cloud infrastructure, created in-house and based in Seoul. This will not only reduce company expenses, but also ensure data security.
Bibliography Networking Case代写
[1] Amazon Web Services, Inc. (2018). Amazon Web Services (AWS) – Cloud Computing Services. [online] Available at: https://aws.amazon.com/?nc1=h_ls [Accessed 20 Sep. 2018].
[2] Armbrust M, Fox A, Griffith R, et al. A view of cloud computing[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2010, 53(4): 50-58.
[3] Avram M G. Advantages and challenges of adopting cloud computing from an enterprise perspective[J]. Procedia Technology, 2014, 12: 529-534.
[4] Fox A, Griffith R, Joseph A, et al. Above the clouds: A berkeley view of cloud computing[J]. Dept. Electrical Eng. and Comput. Sciences, University of California, Berkeley, Rep. UCB/EECS, 2009, 28(13): 2009.
更多其他: 数据分析代写 润色修改 代写案例 Assignment代写 Case study代写 Report代写



您必须登录才能发表评论。